Business process modeling for e-health describes how a business completes missions or tasks. A single model focuses on a one business task and its completion. It takes many process models to illustrate how a business carries out its daily functions.
Processes can be made up of many actors (people, organizations or even systems) simultaneously performing a wide array of tasks. The actors must complete their tasks in a logical, coordinated process to accomplish the overall goal. Most processes have critical decision points where the process flow can either focus on the status of the system or a specific process execution.
A process can look very different when described from the viewpoint of different actors. A business process modeling methodology needs to be able to represent these different aspects of a process.
Business Process Modeling Benefits
The visual aspect of business process modeling makes it critical in the e-medicine arena. Some popular applications for this practice are:
- Baseline for continuous process improvement
- Knowledge retention and learning moving forward
- Process visualization
- Constructing a framework for metrics
- Compliance, audit and assessments
BPM Methodologies
Business process models can be instrumental in the re-engineering process. They can be used to develop various simulations for testing processes on inputs that have yet to occur. They can also be used to create systems automating the very processes they model. Programmers can use the process model as a guide in developing information systems.
Some common methodologies making use of business process modeling are:
- Data Flow Diagrams (DFD): A graphic representation of the flow of data through an information system. A DFD is often used as the opening step to create a system overview.
- Control Flow Diagrams (CFD): A diagram describing the control flow of a business process or review.
- Functional Flow Block Diagrams: A multi-tiered, time-sequenced, step-by-step diagram of a system’s functional flow.
- Unified Modeling Language (UML): A software engineering modeling language created to standardize the visual design of systems.
- Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN): BPMN supports business process management for both technical and business users by providing a notation decipherable by both groups.
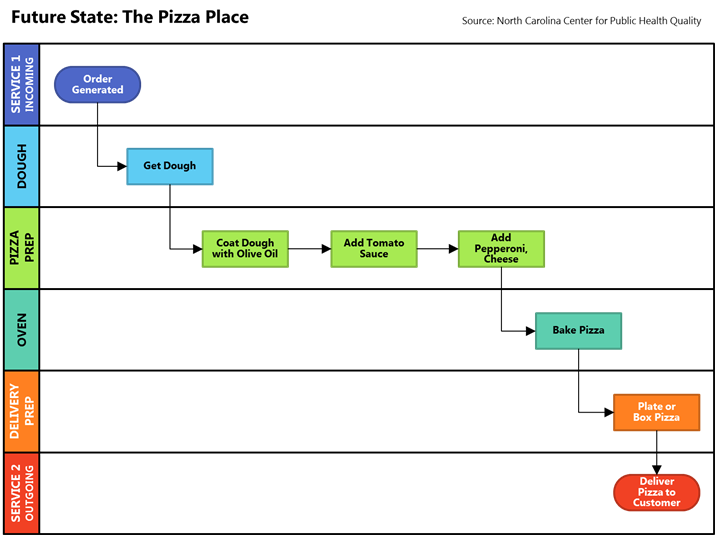
Swim Lane Diagrams
Swim lane business process maps are flow charts showing an organization’s structure. A swim lane is a visual tool used in process flow diagrams, differentiating and assigning responsibilities for the sub-processes of a business plan. Swim lanes can be sorted and arranged either horizontally or vertically.
Swim lane flowcharts differ from other flowcharts because their processes are sorted visually by placing them in their own areas labeled lanes. Parallel lines break the chart into those lanes, with each one representing a person, group or sub-process. Lanes are then labelled to show company structure and organization.
When used to diagram a business process involving more multiple departments, swim lanes clarify the needed steps and who is responsible for them. They also show how delays or mistakes are most likely to come about.